Part production requires careful consideration and planning regarding both the material and process selection. Injection molding vs extrusion is a popular debate because both processes can create repeatable plastic parts at a competitive speed. However, they have some differences as well.
The following text will take a brief look at the main differences between the two processes and discuss which one is the better alternative for part production.
The Main Differences Between Extrusion and Injection Molding
Both extrusion and injection molding are common plastic parts production processes. However, there are significant differences between the two methods pertaining to the process fundamentals, compatibility, strength, and precision. All these factors combine to affect the overall cost and time of the process, which in turn affects the overall costs and capabilities of both methods.
Process
The basics of both processes are the same. Plastic is heated to deform and take the shape of a certain dye, but this is where the similarities between injection molding and extrusion end. The remaining processes are entirely different and require different approaches.
Extrusion, for instance, melts the plastic and pushes it through a certain shape. Resultingly the extruded product, called an extrudate, takes the form of the dye and cools down to solidify.
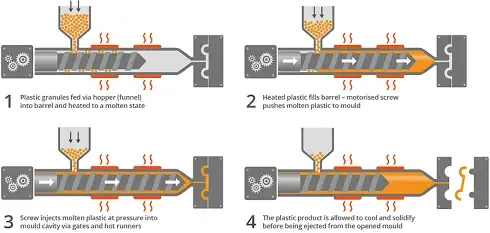
The injection molding process is completely different. The plastic does melt but it’s not pushed through a dye or any other shape. Instead, the liquified plastic goes inside the injection mold with cavities of the required shape. The plastic then cools down inside the mold to solidify and is finally ejected for the next cycle. The process takes place in 4 states and the picture below depicts those.
Compatible Plastics
Injection molding produces almost all thermoplastics and most thermoset plastics. This enables the production of permanent and recyclable components like nylon and acrylic. Extrusion only supports thermoplastics like PVC.
Melt Strength
The melt strength is an important parameter when it comes to plastic-related processes. By comparison, the melt strength for injection molding is lower than that of extrusion because the product is ready by the time it exists in the mold cavity.
Extrusion is different because the product doesn’t get cured and may even require some subsequent processing like thermoforming depending on the application. Therefore, the melt strength requirements for extrusion are quite high when compared to that for injection molding.







